Java 开发者 速通 Python
字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
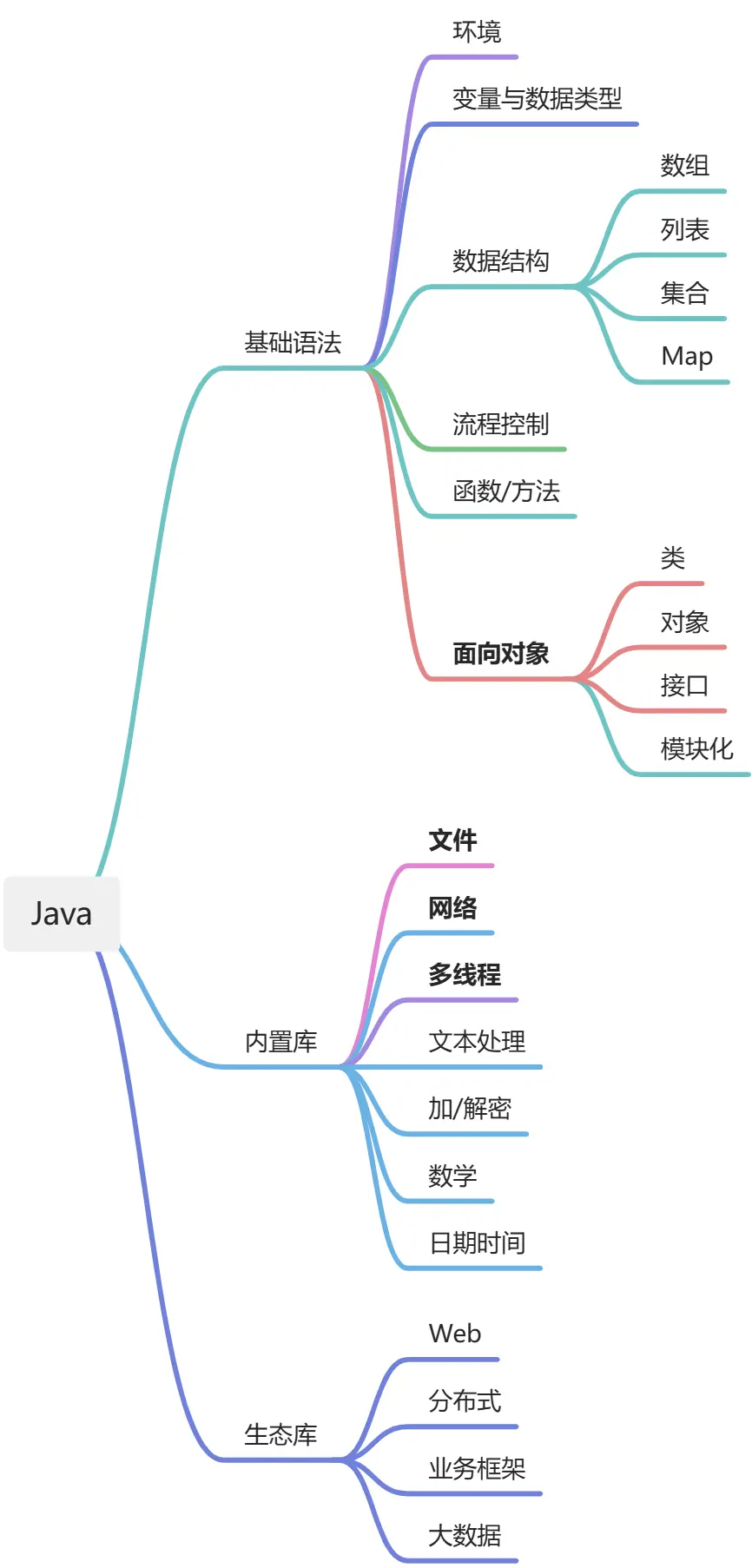
Java 语法体系
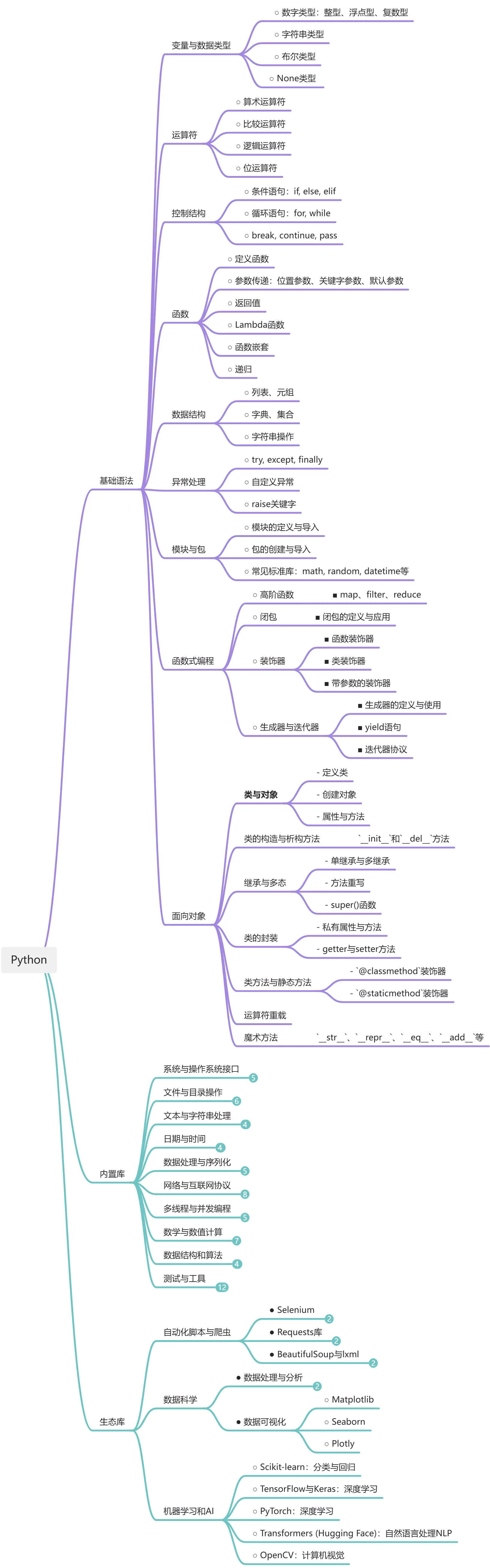
Python 语法体系
变量与数据类型
Python 是动态型语言,变量不需要声明类型
python
# x 是整数 10,类型是 : <class 'int'>
x = 10
# y 是浮点数 3.14,类型是 : <class 'float'>
y = 3.14
# name 是字符串 Alice,类型是 : <class 'str'>
name = "Alice"
# fruits 是数组 ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'],类型是 : <class 'list'>
fruits = ["apple","banana","orange"]
# coordinates 是元组 (10, 20),类型是 : <class 'tuple'>
coordinates = (10,20)
# person 是字典 {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30},类型是 : <class 'dict'>
person = {"name":"Alice","age":30}
# unique_numbers 是set集合 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5},类型是 : <class 'set'>
unique_numbers = {1,2,3,4,5}
print("=============================================")
# 类型转换
# Python 提供了内置的类型转换函数,可以在不同类型之间转换
# 整数转浮点数
int_to_float = float(x)
# 字符串转整数
str_to_int = int("123")
# 列表转元组
list_to_tuple = tuple(fruits)
# 字符串与整数运算
# 不能之间运算,通过转换数据类型实现
str_and_int = name + str(x) # 将整数 x 转为字符串再与 name 拼接
print(f"字符串与整数拼接: {str_and_int}")运算符
算术运算符
python
x = 10
y = 5
# 加法
addition = x + y # 15
# 减法
subtraction = x - y # 5
# 乘法
multiplication = x * y # 50
# 除法(浮点数除法)
division = x / y # 2.0
# 地板除(取整除)
floor_division = x // y # 2
# 取余(模运算)
modulus = x % y # 0
# 幂运算
exponentiation = x ** y # 1000比较运算符
python
a = 15
b = 10
# 等于
a == b
# 不等于
a != b
# 大于
a > b
# 小于
a < b
# 大于等于
a >= b
# 小于等于
a <= b逻辑运算符
python
x = True
y = False
# 与运算
x and y
# 或运算
x or y
# 非运算
not x赋值运算符
python
z = 10
# 简单赋值
z = z + 5
# 加法赋值
z += 5
# 减法赋值
z -= 3
# 乘法赋值
z *= 2
# 除法赋值
z /= 4
# 地板除赋值
z //= 2
# 取余赋值
z %= 3
# 幂赋值
z **= 2位运算符
python
x = 10 # 二进制: 1010
y = 4 # 二进制: 0100
# 按位与
# x & y: 0 (二进制: 0b0)
bitwise_and = x & y
# 按位或
# x | y: 14 (二进制: 0b1110)
bitwise_or = x | y
# 按位异或
# x ^ y: 14 (二进制: 0b1110)
bitwise_xor = x ^ y
# 按位非
# ~x: -11 (二进制: -0b1011)
bitwise_not = ~x
# 左移
# x << 2: 40 (二进制: 0b101000)
left_shift = x << 2
# 右移
# x >> 2: 2 (二进制: 0b10)
right_shift = x >> 2成员运算符
python
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# in 运算符
in_operation = 3 in my_list
# 3 in my_list: True
print(f"3 in my_list: {in_operation}")
# not in 运算符
not_in_operation = 6 not in my_list
# 6 not in my_list: True
print(f"6 not in my_list: {not_in_operation}")身份运算符
python
x = [1, 2, 3]
y = x
z = [1, 2, 3]
# is 运算符
is_operation = x is y # True
print(f"x is y: {is_operation}")
# is not 运算符
is_not_operation = x is not z # True
print(f"x is not z: {is_not_operation}")控制结构
条件语句
python
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("你是成年人")
else:
print("你是未成年人")
# 使用 elif 进行多个条件判断
score = 85
if score >= 90:
print("成绩优秀")
elif score >= 80:
print("成绩良好")
elif score >= 60:
print("成绩合格")
else:
print("成绩不合格")循环语句
python
# for 循环遍历列表
fruits = ["apple","banana","orange"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# while 循环打印数字
counter = 1
while counter < 10:
print(counter)
counter += 1控制循环语句
python
# 使用 break 跳出循环
for i in range(20):
if i == 6:
break
print(i)
# 使用 continue 跳出当前循环
for i in range(10):
if i == 6:
continue
print(i)
# 使用 pass 占位符,用于空代码块,不执行任何操作
for i in range(1,4):
if i == 2:
pass
else:
print(i)循环嵌套语句
python
# 使用嵌套 if 语句和循环语句打印一个乘法表
print("打印一个 1 到 5 的乘法表")
for i in range(1,6):
for j in range(1,6):
print(f"{i} * {j} = {i * j}",end="\t")
print() # 换行match_case 模式匹配
python
def evaluate_grade(grade):
match grade:
case "A": print("表现优异")
case "B": print("表现良好")
case "C": print("表现及格")
case "D": print("不及格")
case _: print("无效成绩")
evaluate_grade("G") # 无效成绩
# 使用 match-case 进行数值范围匹配
def categorize_age(age):
match age:
case age if age < 13:
print("你是儿童。")
case age if 13 <= age < 18:
print("你是青少年。")
case age if 18 <= age < 60:
print("你是成年人。")
case age if age >= 60:
print("你是老年人。")
case _:
print("输入的年龄无效。")函数
简单函数
python
def sayHello(name):
print(f"Hello, {name}")
sayHello("Tom")有返回值的函数
python
def add(a,b):
return a+b
print(add(1,2))默认参数值
python
def greet(name="Alice"):
print(f"Hello, {name}")
greet() # Hello, Alice
greet("Jack") # Hello, Jack可变参数 *args 和 **kwargs
python
# 计算所有数字的和
def sum_all(*args):
print(sum(args))
sum_all(1,2,3,4) # 10
# 打印任意数量的关键字参数
def print_kw(**kwargs):
for key,value in kwargs.items():
print(f"{key} : {value}")
print_kw(name="Tom",age=18,city="重庆")
# 输出
# name : Tom
# age : 18
# city : 重庆递归函数
python
# 计算阶乘
def factorial(n):
if n == 0 or n == 1:
return 1
return n * factorial(n - 1)
print(factorial(4))lambda 函数
python
# 使用 lambda 排序一个列表,按第二个元素排序
tuples = [(1,2),(3,1),(4,5)]
tuples.sort(key=lambda tuple:tuple[1])
print(f"排序后的列表:{tuples}")函数的作用域
python
x = 10
def example():
x = 5
print(x) # 5
example()
print(x) # 10闭包
python
def outer_function(x):
def inner_function(y):
return x + y
return inner_function
close_function = outer_function(10)
result = close_function(5)
print(result) # 15
print(close_function(8)) # 18数据结构
包括列表(list)、元组(tuple)、字典(dict)、集合(set),以及它们的常用操作,如增、删、查、改等。
列表 list
python
fruits = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橙子", "葡萄"]
# 增加元素
fruits.append("草莓") # 在列表末尾添加元素
fruits.insert(2, "梨") # 在指定位置插入元素
print(len(fruits))
# 删除元素
fruits.remove("香蕉") # 删除指定元素
del fruits[1] # 删除指定索引的元素
# 查找元素
index_of_orange = fruits.index("橙子") # 查找元素的索引
print(f"橙子的位置: {index_of_orange}")
# 修改元素
fruits[1] = "柚子" # 修改指定索引的元素
# 遍历列表
print("修改后的水果列表:")
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
# 列表切片
print(f"前两个水果: {fruits[:2]}") # 切片操作元组 tuple
python
coordinates = (10.0, 20.0, 30.0)
# 元组是不可变的,因此无法修改,但可以访问元素
print(f"第一个坐标值: {coordinates[0]}")
# 查找元素的索引
index_of_20 = coordinates.index(20.0)
# 元组切片
print(f"坐标的前两个值: {coordinates[:2]}")字典 dict
python
person = {"name": "Alice", "age": 25, "city": "北京"}
# 增加键值对
person["job"] = "工程师"
# 删除键值对
del person["city"]
# 查找值
name = person["name"]
print(f"姓名: {name}")
# 修改值
person["age"] = 26
# 遍历字典
print("修改后的字典:")
for key, value in person.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
# 获取所有键或值
keys = person.keys()
values = person.values()
print(f"所有键: {keys}")
print(f"所有值: {values}")集合 set
python
fruits_set = {"苹果", "香蕉", "橙子"}
# 增加元素
fruits_set.add("葡萄")
# 删除元素
fruits_set.discard("香蕉") # 不存在时不会报错
# 集合运算
other_fruits = {"苹果", "草莓", "香蕉"}
union_fruits = fruits_set.union(other_fruits) # 并集
intersection_fruits = fruits_set.intersection(other_fruits) # 交集
difference_fruits = fruits_set.difference(other_fruits) # 差集综合操作
python
# 使用列表和字典存储多个学生的信息
students = [
{"name": "Tom", "age": 18, "score": 88},
{"name": "Jerry", "age": 19, "score": 92},
{"name": "Alice", "age": 17, "score": 95}
]
# 根据成绩排序 从大到小
students_sorted = sorted(students, key=lambda student: student["score"], reverse=True)
print("按成绩排序后的学生信息:")
for student in students_sorted:
print(f"{student['name']} - {student['score']}")异常处理
python
# 异常处理案例
# 1. 基本的异常处理
print("---- 基本的异常处理 ----")
try:
# 尝试除以零
result = 10 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(f"错误: {e}") # 捕获并打印除以零的错误
# 2. 捕获多个异常
print("\n---- 捕获多个异常 ----")
try:
# 尝试打开一个不存在的文件
with open("不存在的文件.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read()
except (FileNotFoundError, OSError) as e:
print(f"错误: {e}") # 捕获文件未找到或其他操作系统相关的错误
# 3. 捕获所有异常
print("\n---- 捕获所有异常 ----")
try:
# 尝试将字符串转换为数字
number = int("abc")
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生了一个错误: {e}") # 捕获所有类型的异常
# 4. else 子句
print("\n---- 使用 else 子句 ----")
try:
number = 10 / 2
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
else:
print(f"计算成功,结果是: {number}") # 只有在没有异常的情况下才会执行
# 5. finally 子句
print("\n---- 使用 finally 子句 ----")
try:
# 尝试访问一个不存在的文件
with open("不存在的文件.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read()
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
finally:
print("无论是否发生异常,finally 都会执行") # 这个部分总会执行
# 6. 自定义异常
print("\n---- 自定义异常 ----")
class NegativeNumberError(Exception):
"""自定义异常,表示数字为负数"""
pass
模块与包
项目结构
python
my_project/
│
├── main.py
├── math_operations/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── basic.py
│ └── advanced.py
└── utils/
├── __init__.py
└── helper.pymath_operations/basic.py
python
# 基础运算模块
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def subtract(a, b):
return a - bmath_operations/basic.py
python
# 高级运算模块
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
def divide(a, b):
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("除数不能为零")
return a / butils/helper.py
python
# 辅助工具模块
def print_welcome_message(name):
print(f"欢迎,{name}!")在 main.py 中导入模块
math_operations/和utils/目录本身是包。我们通过包含__init__.py文件(即使是空的)来告诉 Python 这些目录是包。- 包中的模块可以通过 from 包名.模块名 import 函数/类 的方式导入
python
from math_operations.basic import add,subtract
from math_operations.advanced import multiply,divide
import utils.helper as helper
def main():
result_add = add(10,5)
result_sub = subtract(10,5)
result_multiply = multiply(10,5)
try:
result_divide = divide(10,0)
except ValueError as e:
result_divide = f"错误,{e}"
helper.print_welcome_message("Alice")
# 输出结果
print(f"加法结果: {result_add}")
print(f"减法结果: {result_sub}")
print(f"乘法结果: {result_multiply}")
print(f"除法结果: {result_divide}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()面向对象
创建一个模拟图书管理系统,涉及多个类来模拟书籍、图书馆、借阅行为等
书籍类
python
# 定义一个书籍类
class Book:
# 类变量,所有实例共享
book_count = 0
# 构造函数 self 就是 this ,每个对象的实例方法,第一个参数必须是 self
def __init__(self, title, author, genre):
# 实例变量,每个实例独有
self.title = title
self.author = author
self.genre = genre
Book.book_count += 1 # 每次创建一个实例,类变量book_count自增1
def __str__(self):
# 用于打印书籍信息
return f"《{self.title}》 作者: {self.author} 类别: {self.genre}"
# 类方法:用于获取书籍的总数
@classmethod
def get_total_books(cls):
return cls.book_count
# 静态方法:不依赖实例或类,可以直接调用
@staticmethod
def is_valid_genre(genre):
valid_genres = ["小说", "科幻", "历史", "儿童"]
return genre in valid_genres图书馆类
python
# 定义一个图书馆类
class Library:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.books = [] # 存储图书的列表
def add_book(self, book):
if not isinstance(book, Book):
raise ValueError("只能添加Book类型的对象")
self.books.append(book)
def list_books(self):
print(f"在{self.name}图书馆中有以下书籍:")
for book in self.books:
print(book)
# 封装:提供借阅书籍的功能
def borrow_book(self, book_title):
for book in self.books:
if book.title == book_title:
self.books.remove(book)
print(f"已借阅书籍: {book}")
return book
print("书籍未找到!")
return None借阅者类和子类
python
class Borrower:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
self.borrowed_books = [] # 存储借阅的书籍
def borrow(self, library, book_title):
book = library.borrow_book(book_title)
if book:
self.borrowed_books.append(book)
def return_book(self, library, book):
if book in self.borrowed_books:
self.borrowed_books.remove(book)
library.add_book(book)
print(f"{self.name} 已归还书籍: {book}")
else:
print(f"{self.name} 没有借阅过此书")
# 子类:借阅者专属的VIP借阅者
class VIPBorrower(Borrower):
def __init__(self, name, vip_id):
super().__init__(name)
self.vip_id = vip_id
# 重写借书方法,VIP借阅者可以借阅多本书
def borrow(self, library, book_title):
print(f"{self.name} (VIP) 正在借阅书籍: {book_title}")
super().borrow(library, book_title)示例程序
python
# 示例程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建一些书籍对象
book1 = Book("Python编程", "John Doe", "科幻")
book2 = Book("机器学习基础", "Jane Smith", "科幻")
book3 = Book("历史的故事", "H.G. Wells", "历史")
# 检查书籍的类别是否合法
print(f"是否有效类别: {Book.is_valid_genre('科幻')}")
# 创建图书馆对象并添加书籍
my_library = Library("我的图书馆")
my_library.add_book(book1)
my_library.add_book(book2)
my_library.add_book(book3)
# 创建借阅者
borrower = Borrower("Tom")
borrower.borrow(my_library, "Python编程")
borrower.return_book(my_library, book1)
# 创建VIP借阅者
vip_borrower = VIPBorrower("Alice", "VIP123")
vip_borrower.borrow(my_library, "历史的故事")
# 查看图书馆的书籍
my_library.list_books()
# 查看图书馆的总书籍数量
print(f"当前图书馆的总书籍数量: {Book.get_total_books()}")扩展:魔术方法
在 Python 中,以双下划线 __ 开头和结尾的方法被称为“魔术方法”或“特殊方法”。 这些方法并不是每个类中都默认存在的,而是由开发者根据需要定义的。 它们主要用于实现特定的行为,使得类可以与 Python 的内置语法和功能进行交互。常见的魔术方法包括:
- init(self, ...): 初始化对象时调用,用于设置对象的初始状态。
- str(self): 定义对象被转换为字符串时的输出格式,例如在 print() 函数中使用。
- repr(self): 定义对象的“官方”字符串表示形式,通常用于调试。
- len(self): 定义对象的长度,例如在 len() 函数中使用。
- getitem(self, key): 允许对象像字典或列表一样通过索引访问元素。
- setitem(self, key, value): 允许对象像字典或列表一样通过索引设置元素。
- call(self, ...): 允许对象像函数一样被调用。
- eq(self, other): 定义对象之间的相等比较操作。
- add(self, other): 定义对象之间的加法操作。
生态库
仓库 : https://pypi.org/
案例:使用 matplotlib 画函数图
shell
# 安装 matplotlib
pip install matplotlib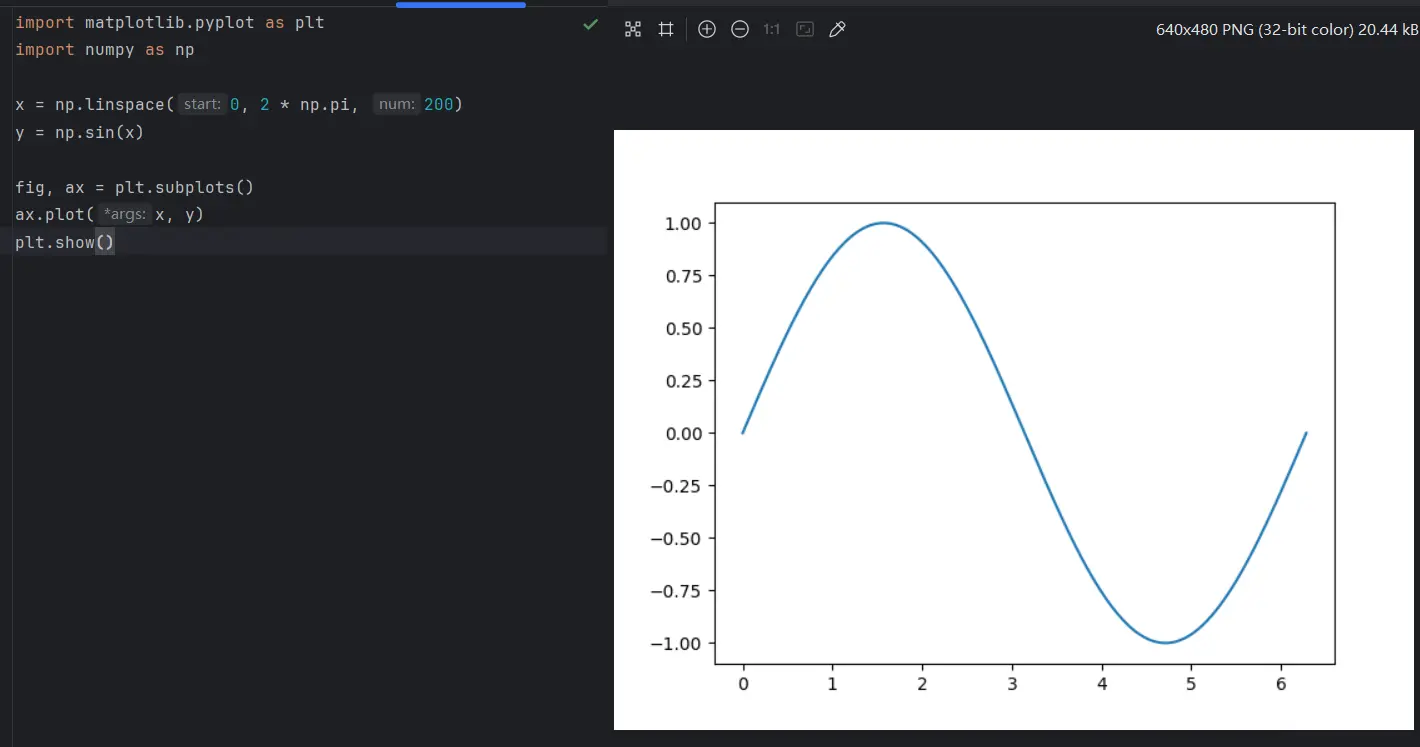
pip 包管理工具
安装包
shell
pip install matplotlib
或
pip install matplotlib=3.7.1查看已安装的包
shell
pip list查看包的详细信息
shell
pip show matplotlib升级包
shell
pip install --upgrade matplotlib卸载包
shell
pip uninstall matplotlib从 requirements.txt 包和版本号管理文件批量安装包
shell
pip install -r requirements.txttxt
matplotlib==3.7.1
numpy==1.24.2
pandas==1.5.3导出已安装的包列表到 requirements.txt 文件中
shell
pip freeze > requirements.txt安装本地包
shell
pip install /path/to/package.tar.gz查看 pip 版本
shell
pip --version